2023 Regulatory Benchmark Report
Executive Summary
The 2023 Veeva MedTech Regulatory Benchmark surveyed worldwide regulatory affairs leaders from medical device and diagnostic companies regarding their strategic role.
Results show that while regulatory affairs (RA) can and should work cross-functionally as a key enabler of innovation and speed-to-market, many medtech regulatory teams are consumed by administrative tasks and inefficiencies. RA is often left to shoulder the burden of gathering, maintaining, and locally storing information required for collaborative tasks. This administrative burden, as well as disjointed data and systems across the organization, reduces productivity and increases compliance risk.
New Product Development
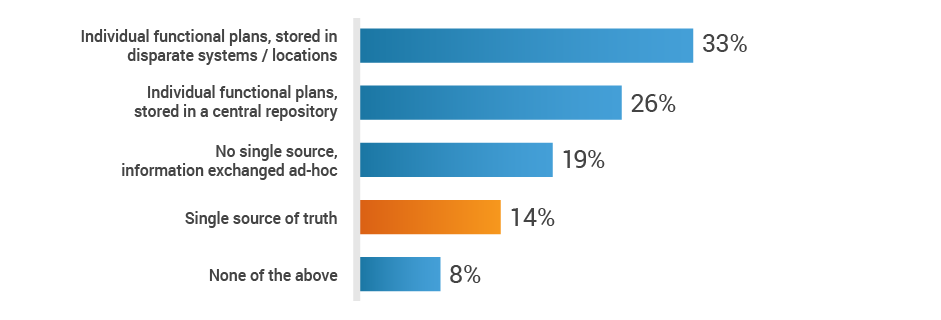
When it comes to new product development, regulatory affairs is inundated with data, including product information, registration information, submission dossiers, and marketing plans. With all of these inputs, medtech organizations are vulnerable to manual process errors and inefficient communication methods. A mere 14% of study participants have a single-source-of-truth platform to exchange strategic plans across functions. With this critical information siloed few RA professionals may know how to prioritize their tasks to benefit the organization.
Do you have a single source of truth, across functions,
to exchange strategic plans for new product development?
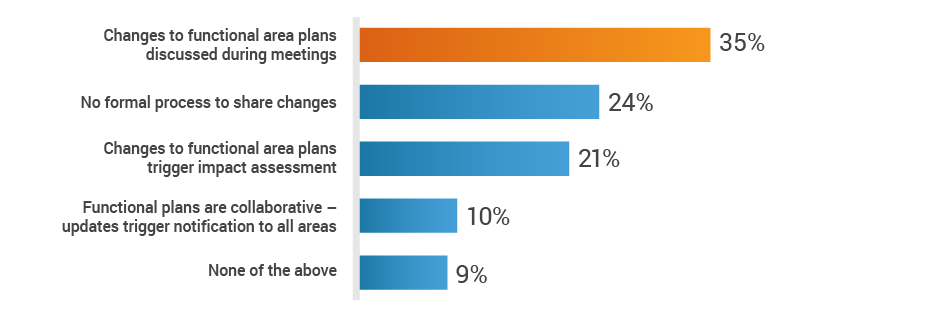
About 35% of respondents rely primarily on status meetings to share plans across functions. This places the onus on individual owners to disseminate vital information, leaving cross-functional teams in the dark regarding new product development activities.
Do you have a cross-functional process to share plans
and inform teams of changes?
Recommendations: Implement a single, unified RIM system for new product submission planning to provide visibility across functions, drive accountability, and ultimately support timely submissions and on-time approvals. Additionally, include the regulatory affairs team in strategic planning to improve collaboration and leverage RA as a critical partner in innovation.

Placing Products on the Market
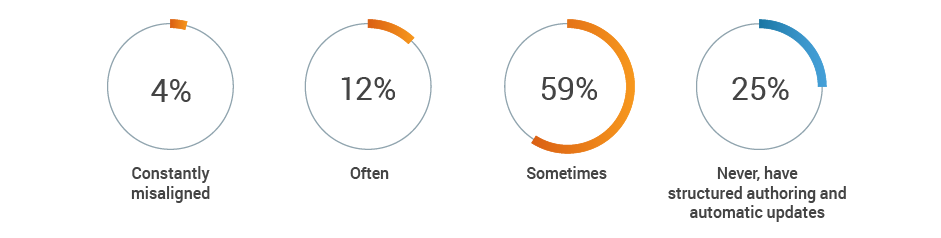
Regulatory remains responsible for the generation and maintenance of critical product information, but often is not kept up-to-date by other functional areas. A combined 75% of respondents report that key content, such as intended use or device description, is at least sometimes misaligned across functions. This increases the risk of inaccurate or incomplete regulatory submissions.
How often is key content, such as intended use or device description,
misaligned across functions?
Additionally, 14% of respondents state that there is no notification process to make regulatory affairs aware of changes to the Design History File (DHF) or Clinical Evaluation Plan (CEP). This means that RA must regularly review these documents and may miss critical changes to the DHF or CEP, which can impact registrations in many markets. This can lead to delays in product approvals, potential compliance violations, and product recalls, ultimately damaging the brand and further costing the company in fines and lost revenue.
How is the RA team made aware of changes to the DHF or CEP?
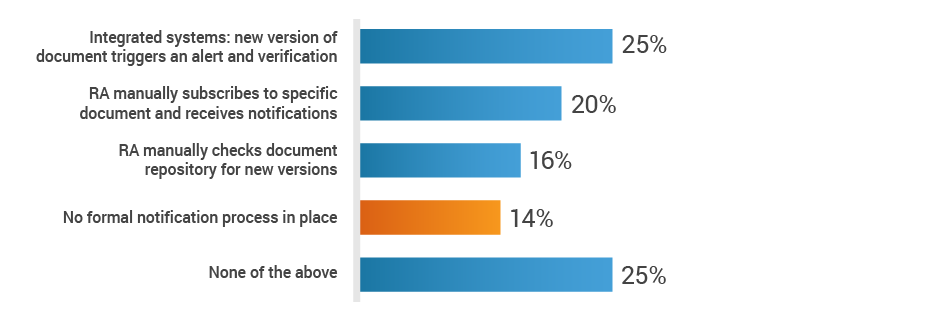
Recommendations: Leverage a single RIM system to enable content reuse, especially key content, such as intended use or device descriptions, increase efficiency, and avoid compliance issues. This will also help RA stay in the loop as they field questions from reviewers or auditors.

Expansion to Other Markets
In-country and global RA teams struggle to communicate in a way that ensures consistency and accuracy of product information across markets. In fact, 35% categorize their organization’s process for critical document exchange between in-country and global teams as “reactive.” Most respondents report that their in-country teams do not have direct access to a single source of truth for documents.
How reactive/proactive is document exchange across
global RA and in-country RA?

Does in-country RA team have access to the single source of truth
to obtain required documents for in-country submissions?

Recommendations: Shift document preparation for global markets from a reactive process to a proactive approach to reduce time spent preparing submissions and enable global teams to be self-sufficient. This could speed approvals and help realize revenue faster across countries.

Supporting Commercial Launch
Regulatory affairs activities don’t stop at the approval of the medical device or diagnostic – all marketing in preparation for commercial launch is also reviewed and approved by RA. However, RA often lacks access to the critical information needed to support the launch of a new product. When asked about the substantiation and claims review process across functions, 34% of RA professionals said reviews are siloed or there’s no clear process in place.
How do you collaborate with cross-functional teams
to substantiate and review claims?
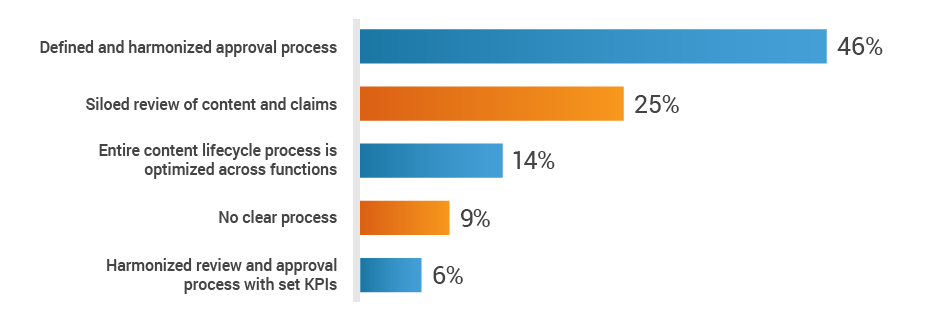
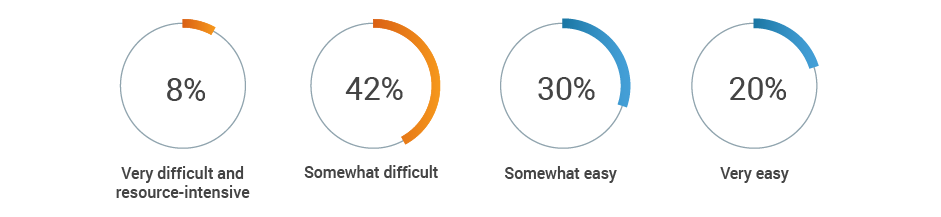
This lack of harmonization can lead to stressful audit situations. Half of respondents say it’s difficult to locate objective substantiation evidence in the event of a product claim audit by a regulatory authority.
If a regulatory authority conducted an audit today of all your product claims,
how difficult would it be to obtain the objective substantiation evidence?
Recommendations: Store and maintain critical information and evidence for claims in a central system with appropriate controls to help facilitate the review process and make it easier to produce evidence during audits.

Sustaining Regulatory Compliance
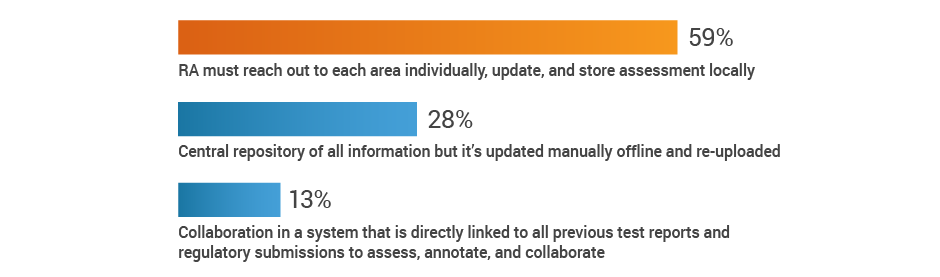
Much of RA’s time is monopolized by keeping abreast of regulatory developments and chasing down the impact to the existing product portfolio, rather than supporting innovation. The study reveals that 59% of respondents have to reach out to individual stakeholders across the organization to gather information and assess the impact of new regulations.
If new regulations require collaboration with other groups, how is that done?
Recommendations: Improve how RA receives new information about the regulatory landscape, so they can focus on assessing the downstream impact on specific products and create action plans.

Renewing Regulatory Approval
The renewal of medical device and diagnostic certifications is a pivotal and recurrent task for regulatory affairs teams, essential for the seamless continuation of global product sales. The consequences of missing a renewal are far-reaching, potentially halting product availability for months, leading to diminished profitability and public health impacts.
If a key person left your organization,
how would that impact your renewal process?
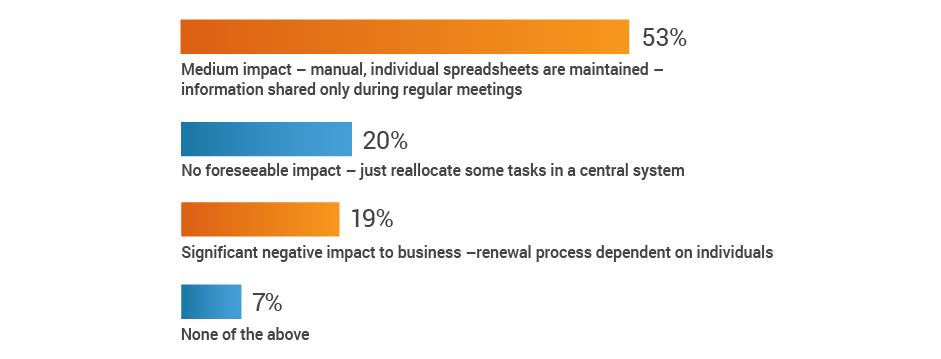
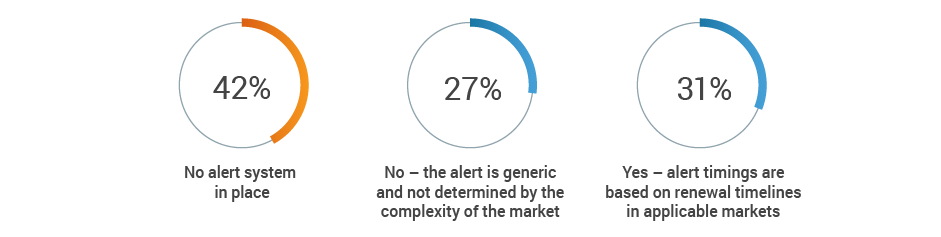
More than half of respondents (53%) recognize the potential for at least a medium impact on renewal processes when a key person departs, with an additional 19% citing significant negative consequences. Given that 42% of respondents also have no renewal alert system, renewal information may be lost when regulatory affairs professionals transition out of roles.
Does your license expiration alert system take into account internal
preparation and expected turnaround time from authorities?
Recommendations: Remove the burden of manually tracking renewals by implementing an automated renewal management system that not only alerts teams to impending renewals but also provides a centralized repository of critical information. This proactive approach will safeguard against disruptions caused by personnel changes and ensure the uninterrupted availability of life-saving and profitable medical devices in the market.

Conclusion
The 2023 study shows that medtech regulatory affairs teams still struggle with issues around visibility into strategic plans, availability of critical content and information, and time-consuming administrative tasks. This impacts all areas that RA supports, including new product development, expansion to other markets, and maintaining compliance.
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve through the introduction of new requirements, regulatory harmonization is more critical than ever before. Having a single source of truth reduces time spent gathering information and allows RA to focus on assessing the impact of regulations on product portfolios to speed submissions.
While other functions may consider RA primarily as a means to initial market approval, maintaining compliance and staying on the market occupy a large amount of RA’s time. Significant time savings can be achieved by using a RIM system to store, validate, and access information. In addition, automated notifications of upcoming renewals can greatly reduce risk, save time, and keep products on the market.
Regulatory affairs should help drive innovation and empower teams to bring new products to market faster. As medtech organizations scale and the regulatory landscape becomes increasingly complex, internal systems, resources, and end-to-end processes will be integral to RA establishing its role as a strategic partner.
Learn how Veeva MedTech’s Vault RIM Platform enables RA teams to take a more strategic role in the organization and fuel innovation.
Survey Methods & Respondents
The study survey consisted of 15 required core questions around medtech regulatory affairs, along with additional demographic questions. Study data includes responses from more than 100 worldwide regulatory affairs leaders at medical device and diagnostic companies. Completion of the survey was voluntary and confidential.
Next: Baxter and Exact Sciences share lessons learned from their organizations’ RIM transformations.